Bulking: A Practical Way to Boost Strength and Size of Muscles
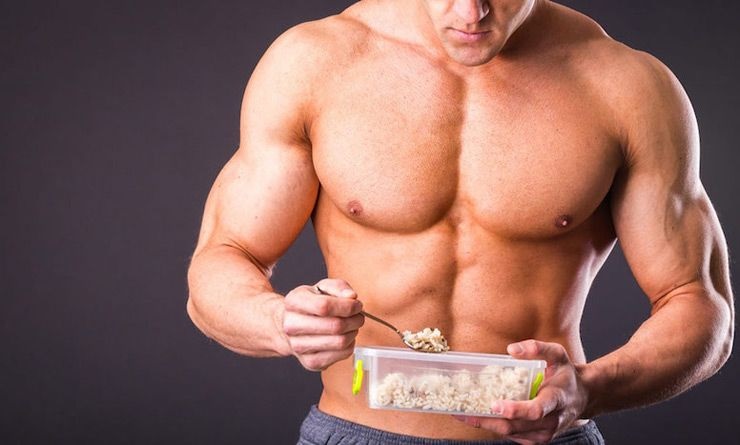

Bulking is a bodybuilding and fitness stage that builds strength and muscle. This is when people eat more calories than they burn, fuelling muscle growth. Reduce fat and maximize muscle growth. Bulking sessions last several months to ensure significant muscle growth. Clean bulking stresses nutrient-dense meals and management of calorie excess, while filthy bulking allows a higher calorie consumption without consideration for nutritional quality.
Nutrition’s Significance in Bulking
Nutrition is key to bulking up. One must consume more calories than they expend, but the kind and composition of those calories matter too. Well-balanced bulking diets include lipids, carbohydrates, and protein. Muscle growth and repair require the RDA of 1.2 to 2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight. Lipids help make hormones and maintain health, but carbohydrates fuel long, strenuous workouts and replenish glycogen. Including lean meats, whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats in the diet will provide the body with vitamins and minerals.
Making a Successful Exercise Program
During bulking, muscular growth demands efficient training. Resistance training, especially with heavy weights and complex movements, is optimal for muscle building. Bench presses, squats, deadlifts, and rows train multiple muscle groups and build strength. Training volume, frequency, and intensity should be carefully calculated to stimulate muscle growth and allow recovery. Every muscle group is exercised two to three times a week with heavy lifting and higher-repetition sets to work different fibers.
Rest and Recuperation Value
Relaxation and recovery are crucial to bulking, but often overlooked. Exercise does not grow muscles. During rests. General health and muscle restoration require 7-9 hours of sleep per night. Training should include rest days to allow muscles to grow and recuperate. Foam rolling, stretching, and massages can also expedite healing and reduce muscle pain. A healthy diet and enough water help rebuild muscles, speeding recuperation.
Monitoring and Adjusting
Monitoring progress ensures the bulking phase succeeds and allows for changes. Regularly monitoring strength, body measurements, and body weight can reveal how well the bulking plan is working. If weight gain is uncontrollable, you may need to cut calories or exercise more. If muscle growth is slow, you may need to eat more or exercise more. Performance logs, body composition assessments, and progress photos can help track and make informed improvements.
Switching from Bulk to Cutting
Moving into a lowering phase following optimal muscle development helps lose fat while maintaining muscle mass. Cutting need a calorie deficit to lose fat. Avoid muscle loss by progressively cutting calories. Resistance training and a high-protein diet are essential to muscle preservation.
Conclusion
A well-planned mix of higher calorie intake, appropriate diet, an organized training schedule, sufficient rest, and frequent progress tracking is required for efficient bulking. After bulking, moving into a cutting phase refines the body by eliminating fat without sacrificing muscular mass. People may successfully enhance their muscle mass and strength and reach their fitness objectives by comprehending and putting these ideas into practice.